HMO Licensing
Key Takeaways Summary:
- Mandatory licensing for larger HMOs and additional requirements by local councils
- Essential safety standards and property management obligations
- Financial implications and penalties for non-compliance
- Step-by-step application process and documentation requirements
- Ongoing compliance and management responsibilities
1. Understanding HMO Basics and Legal Requirements
HMO (House in Multiple Occupation) properties form a crucial part of the UK’s rental market, but they come with specific legal obligations. Understanding these requirements is essential for any landlord considering this investment route.
The Housing Act 2004 defines an HMO as a property rented to three or more tenants from two or more households, sharing facilities like bathrooms and kitchens. This definition encompasses various property types, from traditional house shares to purpose-built student accommodation.
Recent legislation changes have expanded mandatory licensing requirements, making it more important than ever for landlords to ensure compliance. Failure to obtain proper licensing can result in significant fines and legal complications.
[Table: Types of HMO Properties]
| Property Type | Description | Typical Tenants |
|---|---|---|
| Student Houses | Shared houses for students | University students |
| Professional House Shares | Shared properties for working adults | Young professionals |
| Bedsit Properties | Individual rooms with shared facilities | Mixed tenants |
| Converted Buildings | Properties split into multiple units | Various tenants |
2. Mandatory Licensing Requirements
Mandatory HMO licensing applies to properties meeting specific criteria. Understanding these requirements is crucial for legal compliance and avoiding penalties.
The current regulations mandate licensing for properties with five or more occupants from two or more households, regardless of the number of storeys. This represents a significant change from previous requirements that only applied to properties of three or more storeys.
Local authorities may impose additional licensing schemes, making it essential to check specific requirements in your area. These schemes can extend licensing requirements to smaller HMOs or specific geographical areas.
3. Safety Standards and Property Management
HMO compliance requires meeting strict safety standards and property management requirements. These standards are designed to protect tenants and ensure proper property maintenance.
Fire safety measures, including fire doors, smoke alarms, and emergency lighting, must be installed and maintained according to current regulations. Regular fire risk assessments are mandatory, and documentation must be kept up to date.
Room sizes and amenity provisions must meet minimum standards, with specific requirements for kitchen and bathroom facilities based on the number of occupants.
[Table: Minimum Room Size Requirements]
| Room Type | Minimum Size (1 person) | Minimum Size (2 persons) |
|---|---|---|
| Bedroom | 6.51 m² | 10.22 m² |
| Living Room | 13 m² | 13 m² |
| Kitchen | 5.5 m² | 7 m² |
4. Financial Implications and Costs
Understanding the financial aspects of HMO licensing is crucial for landlords planning their investment strategy.
License fees vary by local authority and property size, typically ranging from £500 to £1,500 for a five-year period. Additional costs may include property modifications to meet required standards and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Non-compliance penalties can be severe, with fines up to £30,000 per offense and potential rent repayment orders.
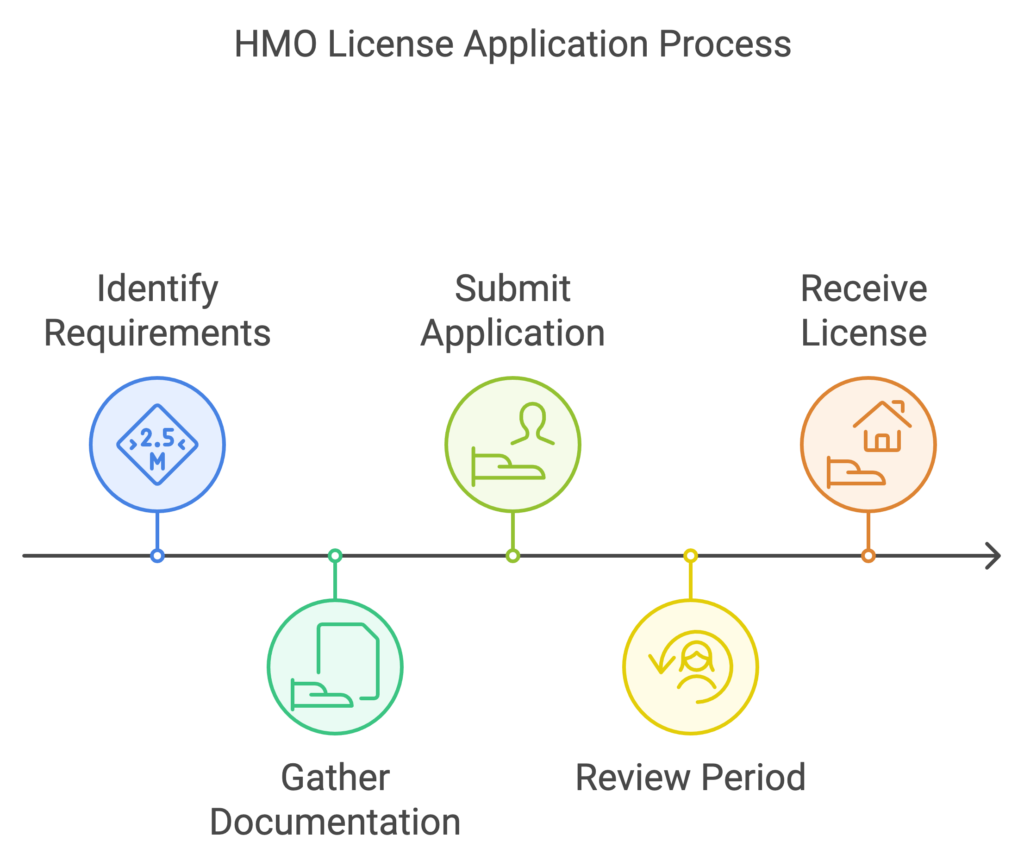
5. Application Process and Documentation
The HMO licence application process requires careful attention to detail and comprehensive documentation. Understanding the requirements beforehand can streamline the process significantly.
Essential documentation includes proof of ownership, floor plans, gas safety certificates, and electrical installation condition reports. Local authorities may require additional documents specific to their region, so it’s crucial to check local requirements.
The application timeline typically spans 8-12 weeks, though this can vary by location and application complexity. Early preparation and organization of documents can help avoid delays.
[Table: Required Documentation Checklist]
| Document Type | Validity Period | Renewal Required |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Safety Certificate | 12 months | Annual |
| Electrical Safety Report | 5 years | Every 5 years |
| Fire Risk Assessment | Ongoing | Annual review |
| Energy Performance Certificate | 10 years | As needed |
6. Ongoing Compliance and Management
HMO regulations UK require continuous monitoring and management to maintain compliance throughout the licence period.
Regular property inspections are essential, with detailed records of maintenance, repairs, and safety checks. Establishing a systematic approach to property management helps ensure nothing is overlooked.
Tenant management and communication play vital roles in maintaining compliance. Clear protocols for handling complaints and maintaining harmonious shared living environments are crucial.
[Table: Maintenance Schedule]
| Task | Frequency | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Alarm Testing | Weekly | Landlord/Agent |
| Emergency Light Testing | Monthly | Qualified Engineer |
| Property Inspection | Quarterly | Landlord/Agent |
| Appliance Testing | Annual | Qualified Engineer |
7. Common Challenges and Solutions
Understanding typical obstacles in HMO management helps landlords prepare effective solutions and maintain profitable operations.
Space optimization and room configuration often present challenges, particularly in older properties. Creative solutions and professional design input can help maximize space while meeting regulatory requirements.
Managing multiple tenancies requires robust systems and clear procedures. Implementing property management software can help streamline operations and maintain accurate records.
8. Future Trends and Changes
The multi-let property UK sector continues to evolve, with new regulations and market trends shaping future requirements.
Environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important, with potential new requirements for energy efficiency and sustainability measures. Planning for these changes can help future-proof your investment.
Technology integration is transforming property management, with smart home systems and digital platforms becoming increasingly prevalent.
[Table: Upcoming Regulatory Changes]
| Area | Expected Change | Implementation Date |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Minimum EPC Rating C | 2025 |
| Fire Safety | Enhanced Requirements | 2024 |
| Room Standards | Updated Specifications | 2024 |
Key Takeaways:
- Thorough documentation and regular updates are essential
- Proactive maintenance prevents costly issues
- Technology adoption improves management efficiency
- Future-proofing investments requires awareness of upcoming changes
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Do I need an HMO licence for my property?
- Answer: If your property is rented to 5 or more people from 2 or more households, you need a mandatory HMO licence. Check with your local authority for additional licensing requirements.
- How long does an HMO licence last?
- Answer: Typically 5 years, but duration can vary by local authority.
- What happens if I operate without a licence?
- Answer: You risk fines up to £30,000, prosecution, and rent repayment orders.
- What’s the process for renewing an HMO licence?
- Answer: Start the renewal process at least 3 months before expiry. You’ll need updated safety certificates, proof of continued compliance, and to pay the renewal fee. The process is similar to the initial application but typically moves faster if there have been no significant changes.
- Can I convert my regular rental property into an HMO?
- Answer: Yes, but you’ll need planning permission for change of use in most cases, plus building regulations approval for any structural changes. You must meet all HMO standards before letting and obtain the licence before tenants move in.
- What fire safety measures are mandatory in HMOs?
- Answer: Requirements include interconnected smoke alarms on each floor, heat detectors in kitchens, fire doors on all bedrooms and kitchens, clear escape routes, fire extinguishers on each floor, and emergency lighting in larger properties. A professional fire risk assessment is also mandatory.
- How often do local authorities inspect HMO properties?
- Answer: Initial inspection occurs during the licensing process, with routine inspections typically every 1-2 years. Additional inspections may occur following complaints or concerns. Some councils operate random spot-checks.
- What room sizes are legally required for HMOs?
- Answer: Single bedrooms must be at least 6.51m², double rooms 10.22m². Rooms under 4.64m² cannot be used as bedrooms. Some local authorities set higher minimum requirements, so check local standards.
- Can tenants make modifications to their rooms?
- Answer: Tenants must get written permission for any modifications. Generally, decorative changes like picture hanging might be allowed, but structural changes are prohibited. All modifications must comply with HMO safety requirements.
- What are the main reasons HMO licence applications get rejected?
- Answer: Common reasons include insufficient room sizes, inadequate fire safety measures, poor property management history, failing to meet local amenity standards, and incomplete documentation. Criminal records or history of housing law breaches can also lead to rejection.




